What are PCBs?
PCB means Printed Circuit Board. It is used to connect electronic components mechanically and electrically. It is a non-conductive material with conductive lines printed or etched.
With the rise of PCB applications reaching far and high, designs for applications that extend beyond simple solutions for signal integrity are big developed. For many industries that have otherwise been inactive in the PCB world, developments in material technology, PCB producing capacities, and the increasing demands for PCB design.
What is a High-Current PCB design?
High-current PCB design is any design in which the physical characteristics of your circuit board, such as your layout, packaging, layer stack-up, interconnections, etc., begin to influence the integrity of your signals.
In this world of PCB design, where you spend most of your time finding the right parts, putting them all on the layout of your board, wiring it with traces, and submitting your files to your distributor. You're possibly designing standard boards at this point, and if anyone were to mention the integrity of the signal, crosstalk, or vibrations, you would probably feel lost. But you could have a high-speed PCB project slapped down on your desk sooner or later. And you better put on your boots when this happens, because you're going to be wading through some pretty deep information. And you better put on your boots when this happens, because you're going to be wading through some pretty deep information. Most of the time, we will deal with the distribution and management of power through the PCB while addressing high-current applications. However, this was a pace that no one, no matter how courageous, had ever visited. Since many of the parts on a dedicated board have their power requirements and would be hard to deal with, combining signals in your PCB was just too difficult a task. Additionally, the supply of printing boards that could accommodate the loads physically was not up to scratch. With the new technologies and growing demand, we are progressing at an incredibly fast pace and are again exploring the depths of combining signals based. We must retain our controls and analysis of the heat and power maps for our designs to ensure that we remain secure within this explosive domain.
Types of PCBs:
There are some types of PCBs:
· Single-Sided
· Double-Sided
· Multi-layer
· Rigid
· Flexible
· Aluminum-backed
1. It is the basic kind of circuit board, which contains only one layer of coating or base substance.
2. Double-sided PCBs, it is most common than single-sided PCBs besides, that they have two-sided ones.
3. Multilayer PCBs are difficult than double-sided PCBs which come with a mixture of single and double-sided boards.
4. In electronics, rigid PCBs are widely used to provide power to the circuits, make them hard and protect them from moving.
5. Flexible PCBs are supple and stretch and move into any shape based on need and requirement.

Image Courtesy: PCBgogo
6. When several flexible PCBs are joining with a set of rigid layers, Rigid-Flex PCBs are created.
7. High-Frequency PCBs are rather different from conventional PCB and are efficient for one GHz transmission of signals.
8. Aluminum-backed PCB is close to copper PCB in some cases, such as Substrates in aluminum-backed PCBs material consist of aluminum or copper.
The main part of High Current PCBs
There are some parts of high current PCBs:
Copper width:
Copper width is one of the basic parts that decided how much a current can hold. More current would be borne by traces of greater width. Commonly, for a board with regular copper thickness, it is a rule of thumb to expect a trace width of 1 mm per amp of current taken.
Copper Thickness:
The real thickness of the traces that are on a PCB is copper thickness. Normally, the default copper thickness is 17.5 microns. It can be 35 and 50microns. The wider the thickness of copper, the less deep the trace must be to bear the same current. More increased copper thickness comes at an added expense but can help save space on your boards because the necessary trace width is much less with greater viscosity.
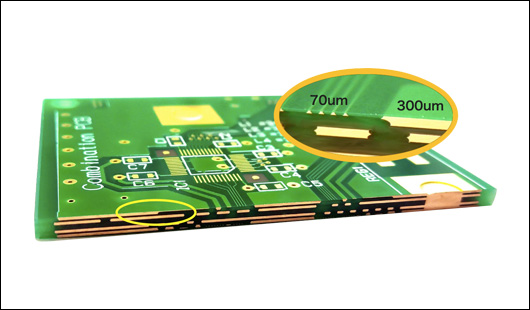
Image Courtesy: PCBgogo
Manufacturer's Technological Capabilities:
The following two points are important for high current boards and should be looked at on the technical capabilities page of your manufacturer.
1. The thickness of copper for the outer layers - this will mean the top and bottom of the two outermost layers on your board.
2. Inner layer of copper thickness - This shows the limits of copper thickness on the inner layers, and large currents also have to be borne by the inner layers, especially for packages such as BGA.
Heat Produced
Heat is the main factor that generated a high current track in PCB. It contributes to the longevity of the board and components. The loss of power in watts can be measured as the trace resistance multiplied by the square of the current that flows through it.
High current PCBs Applications
Electronics are an essential part of our lives nowadays. Form smartphones to home appliances we need electricity as it plays the main role. PCBs are the main factor of electricity. It is the basis of most electronic devices today. This versatility enables the operation of PCBs in many powers and applications. In more information below, we have discussed a few of these applications:
Medical Equipment:
Electronics is a major contributor to the health-care industry, acting as diagnostic, control, and treatment systems. As electronics grow to become more powerful and compact, the medical uses of these electronic devices continue to develop, leading to countless new possibilities. To satisfy the specific constraints of medical equipment, PCBs within the medical industry is highly technical. Medical PCB, also referred to as HDI PCB, appears to be a high-density interconnect PCB specialty. Adjustable base materials can also be made from medical PCBs, allowing PCBs to flex during use, which can be necessary for both internal and external medical devices. In addition to compliance with stringent medical regulations, repeatability and reliability are two important qualities that medical PCB suppliers must attain. Here are some most common medical PCBs:
Monitors: Blood, glucose, heart rate, and blood pressure monitors are including personal and health care monitors.
Chemical Instruments: To study illness and test patient effects, medical science uses various scientific methods. These include, among other items, electronic microscopes, photometers, and generator and compressor control systems.
Control systems: The equipment is electronically controlled to regulate the mixture, flow rate, and immunity of fluid.
Scanning: PCB-based electronics are also used by CT scanners and ultrasonic technology.
Internal Equipment: Heart stents and similar internal medical devices preserve patient wellbeing at their cores, powered by minuscule PCBs.
Electronics for Customers:
Smartphones, computers, and the many other consumer goods people use every day need PCBs to operate. As electronics need more in our daily products PCBs became an essential part of our lives. Companies produce smaller and smaller smartphones and laptops with many unique technologies that involve tiny PCBs with large link volumes. PCBs are used in a wide variety of consumer goods, such as:
Computers and Laptop Computer used every field of life in the century. PCBs is used in both desktop and laptop computer. They serve as the basis for many components of internal computers. All these components are directly connected to the motherboard which is also a PCB.
Communications devices: Communication devices such as mobile phones, radio, television, and other devices need PCBs to work.
Home appliances: Many home equipment like fridge, a/c, and microwave used PCBs.
Industrial Equipment:
In the industrial sector, PCBs also need to be extremely high-powered and sufficiently robust to withstand the harsh conditions that occur in industrial installations. In the industrial sector, PCBs also need to be extremely high-powered and sufficiently robust to withstand the harsh conditions that occur in industrial installations.
Sea application:
To work, all kinds of marine vessels and systems depend on PCBs. This includes small boats, large cargo ships, warships, navigation equipment, and communications systems.
Safety appliances:
PCBs are used in every safety appliance. Such as electronic door locks, security cameras, and smoke detectors, etc.
Telecommunications applications:
Due to the many different types of equipment used in the industry, the telecommunications industry uses a wide range of types of PCBs. Telecom tower, Office communications equipment and LED displays and indicators are included in telecommunication equipment.
Military and Defense Applications:
In military applications, the PCBs used must be exceptionally reliable and safe. They may be exposed to extreme circumstances and may play a role in national security. Due to their ability to withstand tough conditions, such as elevated temperatures, the military uses materials such as high-temperature laminates, aluminum, and copper.
Advantages of High Current PCBs
Here are different advantages of PCBs such as:
· Easy repairing
· Time-saving
· Resistance of movement
· Saving of wire
· Good connection
· Prevent from short circuit
· Low noise
· Low cost
· Reliability
Engineers at PCBgogo are highly specialized not only in quick-turn PCB prototype and PCB assembly, but also medium and small volume PCB fabrication. PCBgogo has three factories, established over 17,000 square meters; fully compliant with the ISO 9001:2015 quality management system, UL certified and committed to adhering to the strictest standards in manufacture and assembly. The company is operating since 2017, PCBgogo has delivered over US $50 million worth of electronic components and prototyping services to more than 100 thousand customers all over the world.